Fingerprints have long been recognised as a vital evidence in forensic sciences, playing a crucial role in crime scene investigations.
Their importance lies in their uniqueness and permanence, allowing for the identification of individuals based on the pattern and ridges on their fingerprints.
The fingerprints are classified into three main types: loop patterns, whorl patterns and arch patterns. Each type has distinct characteristics that contribute to the identification process.
Collecting fingerprints at crime scenes possess it challenges, but various techniques and tools are employed to preserve and collect them.
Identifying fingerprints involves the meticulous comparison and analysis of ridge patterns, aided by National Automated Fingerprint Identification Systems (NAFIS).
Forensic experts in our lab, play a very crucial role in this identification process, utilising their expertise to match and analyse fingerprints accurately.
Further advancements in fingerprint analysis technology and chemical methods for developing latent fingerprints continue to enhance the techniques used in identifying these crucial pieces of evidence.
The study of fingerprints and their identification at crime scene is an ever-evolving field that continues to contribute significantly to forensic sciences.
Listed below is all you need to know about fingerprints, types and identification at Crime Scenes:
Fingerprints play a crucial role in forensic science, aiding in the identification of individuals at crime scenes.
There are three main types of fingerprints: loop patterns, whorl patterns and arch patterns.
Loop patterns are the most common type, characterised by ridges that enter and exit from the same side.
Within this category, there are ulnar loops, where the ridges flow towards the little finger, and radial loops, where the ridges flow towards the thumb.
Whorl patterns are circular or spiral in shape, with ridges that form concentric circles or spirals. They can be further classified as plain whorls, central pocket loops, or double loops, depending on their specific characteristics.
Arch patterns are the least common type, featuring ridges that enter on one side and exit on the other, forming a wave-like pattern. There are two subtypes of arch patterns: plain arches and tented arches.
Understanding these different fingerprint types is essential for identifying individuals at crime scenes.
By carefully analysing the patterns and minutiae of these unique marks, forensic experts are able to make accurate identifications, aiding in the pursuit of justice.
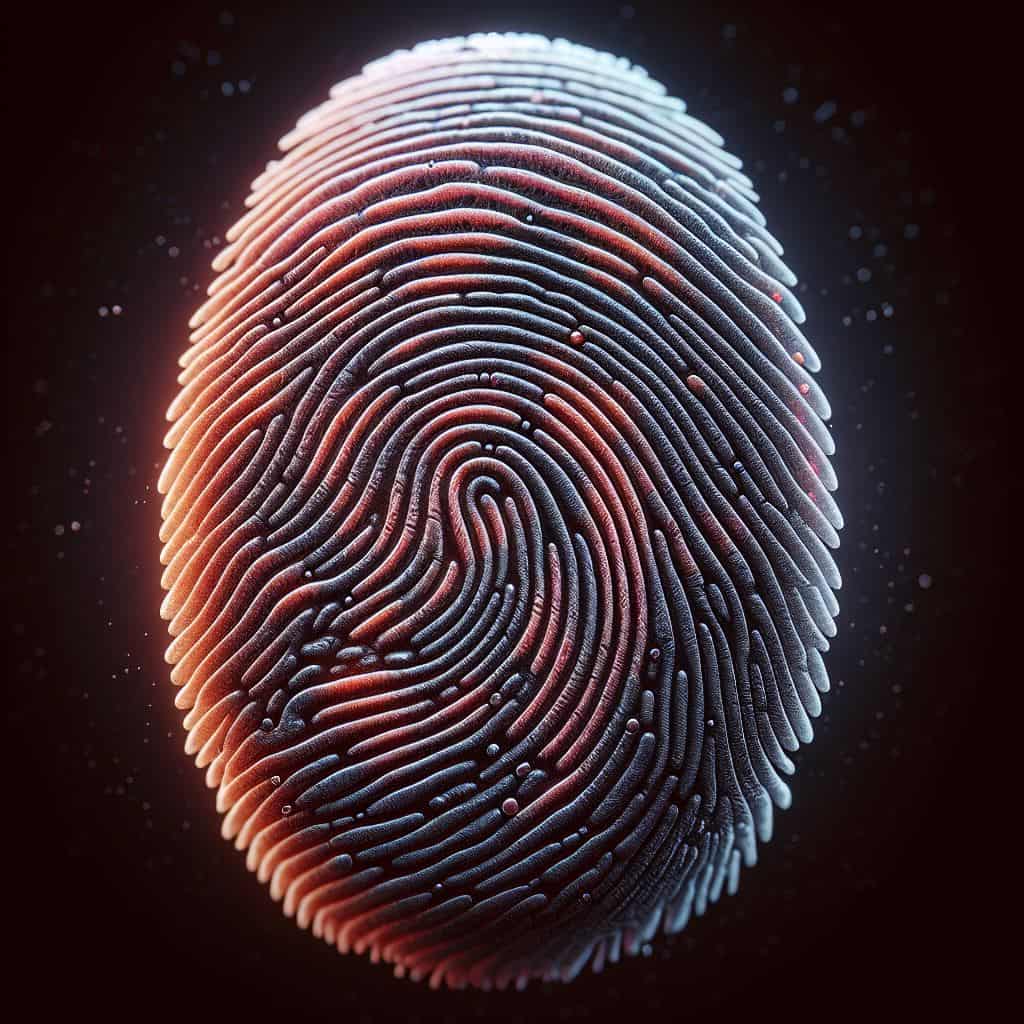

Loop patterns are one of the three main types of fingerprints, alongside whorl and arch patterns. These patterns are characterised by one or more ridges that enter from one side of the finger, loop around and exit from the same side they entered.
Loop patterns can be further classified into radial and ulnar loops, depending on the direction of the loop.
Radial loops are formed when the ridges enter from the thumb side of the finger and exit toward the little finger side.
Ulnar loops, on the other hand have ridges that enter from the little finger side and exit towards the thumb side.
These loop patterns are common, accounting for approximately 60-65% of all the fingerprints.
When it comes to identifying loop patterns at crime scenes, forensic experts employ various techniques and tools, they carefully study the shape, size and direction of the loops, as well as any unique characteristics within them, such as delta points and ridge counts.
By thoroughly analyzing these loop patterns, experts can make accurate identifications and help solve crimes based on fingerprint evidences.
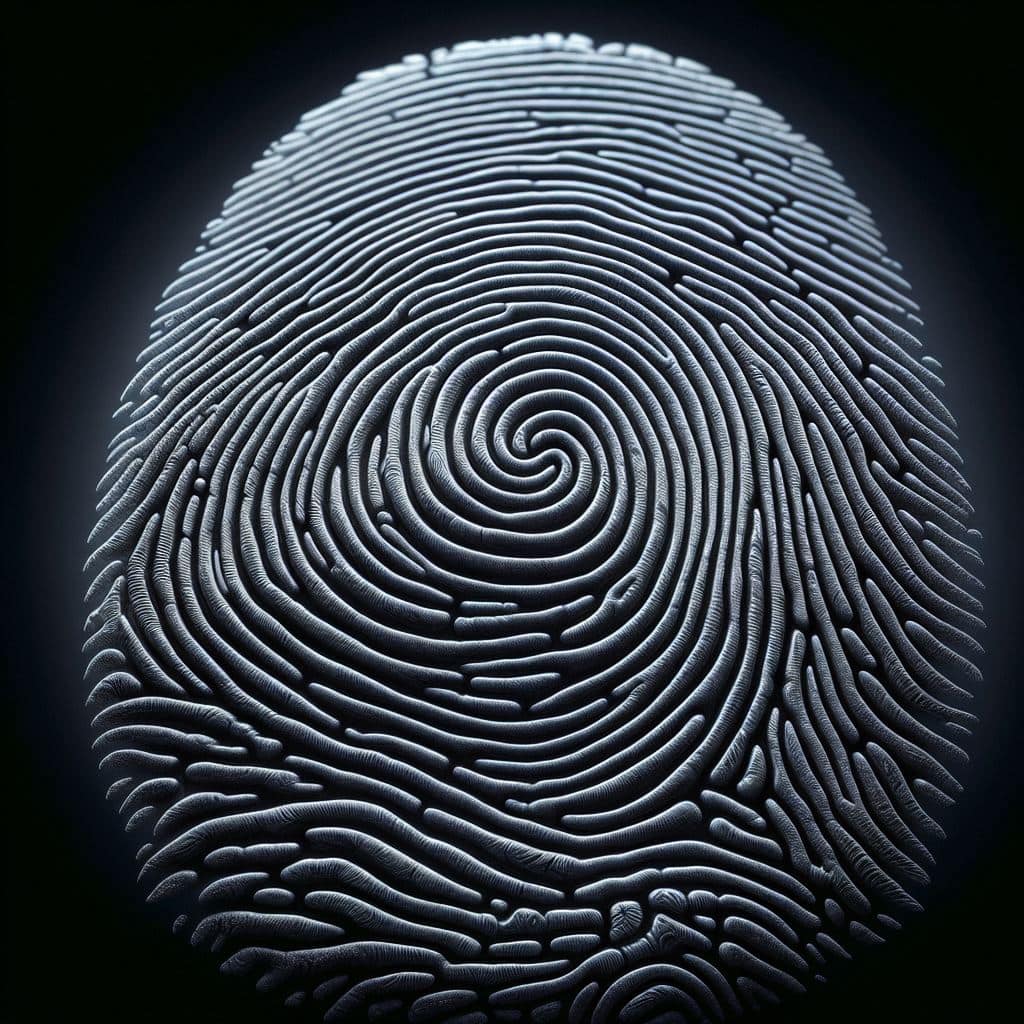

Whorl patterns are one of the three main types of fingerprints, the others being loop patterns and arch patterns.
Whorl patterns are characterised by circular or spiral ridges, creating a distinct pattern that can be used for identification.
There are several subcategories of whorl patterns, including plain whorls, central pocket loops, double loops, and accidental whorls.
Each subcategory has its own unique characteristics and can provide valuable information in forensic investigations.
At a crime scene, identifying whorl patterns can be crucial in determining the identity of a suspect or linking them to the scene.
Forensic experts use various techniques and tools to collect fingerprints, ensuring their preservation for analysis. The comparison and analysis of fingerprints play a key role in identifying individuals involved in criminal activities.
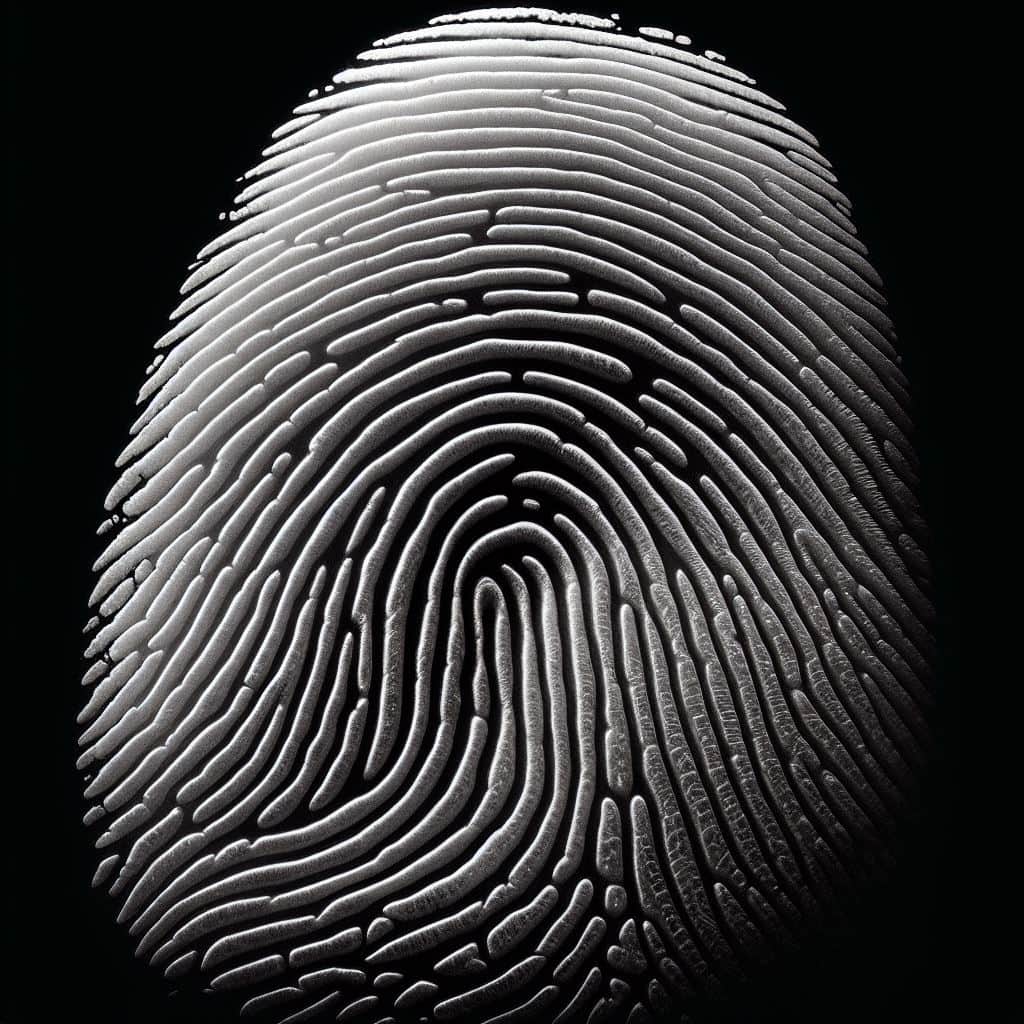

Arch patterns are an important aspect of fingerprint identification at crime scenes. These patterns are characterised by ridges that enter from one side of the fingerprint and exit on the other side.
Unlike loops and whorl patterns, arch patterns do not have any significant deltas or core points. They are relatively less common and can be further classified into two subtypes: Plain arches and tented arches.
Plain arches have a smooth and rounded appearance, with ridges forming a consistent curve. On the other hand, tented arches have a more pointed appearance due to a central thrusting ridge.
Understanding arch patterns and their identification plays a vital role in forensic science. By accurately analyzing and classifying different types of fingerprints, investigators can make significant progress in solving crimes and bringing justice to victims.
Techniques for preserving fingerprints at crime scene involve various methods to ensure their visibility and prevent contamination. These techniques include dusting, which uses a fine powder to highlight fingerprints on smooth surfaces, and chemical methods that react with the sweat and oils in fingerprints.
Additionally, adhesive materials like transparent tape or gel lifters are used to lift the prints for transfer to a cord or other suitable surface for preservation and further analysis.
Tools used for fingerprint collection include powders, brushes, magnifiers and lifting materials. Powders are used to enhance visibility and aid in the collection of prints. Brushes help to evenly distribute the powder, while magnifiers assist in examining and photographing the prints.
Lifting materials, such as gel lifters or adhesive tape, are used to carefully lift and preserve prints from various surfaces without damaging them. While collecting fingerprints at crime scenes, forensic experts encounter several challenges.
Environmental conditions, such as heat or humidity, can impact the visibility and quality of fingerprints. Contaminants on the surface can also hinder the detection of prints. Additionally, the presence of irregular or textured surfaces makes it more difficult to collect clear and usable prints.
Overcoming these challenges requires expertise, meticulousness, and the careful application of appropriate techniques and tools.
Preserving fingerprints at crime scenes is crucial for successful identification and analysis. Several techniques are employed to ensure their preservation. One common method is dusting, where a fine powder is applied to the object or surface to reveal the latent fingerprints.
Another technique involves using chemicals, such as ninhydrin or iodine, to develop fingerprints on porous materials. In some cases, forensic experts may use cyanoacrylate fuming, which involves fuming the object with superglue to visualise the prints.
Additionally, electrostatic lifting can be employed to capture and preserve fingerprints on smooth surfaces without damaging the evidence. These techniques have proven to be effective in preserving fingerprints at crime scenes, enabling forensic experts to further analyse and identify them accurately.
In order to collect fingerprints at crime scenes, forensic investigators rely on a variety of tools. These tools are specifically designed to ensure accurate and effective collection of evidence. One commonly used tool is the fingerprint brush, which is made from fine fibers and is used to gently sweep over surfaces to collect any visible or latent fingerprints.
Another tool is fingerprint powder, which is carefully applied to surfaces and adheres to the oils in fingerprints, making them easily visible. Additionally, forensic investigators may use fingerprint lifting tape to carefully peel off and preserve the collected fingerprints for further analysis.
These tools, among others, play a crucial role in the process of collecting fingerprints at crime scenes, enabling investigators to gather vital evidence for identification and analysis.
Collecting fingerprints at crime scenes can present several challenges. First, the nature of the surface where the fingerprint is lift plays a crucial role. Different surfaces, such as glass, plastic or paper, require different collection techniques to ensure preservation and accuracy.
Additionally, environmental factors like temperature and humidity can affect the quality and visibility of fingerprints, making them more challenging to collect.
Another challenge in collecting fingerprints is the pressure of latent prints. These are invisible prints left behind from sweat, oil or other substances on a surface, Detecting and collecting these prints often require specialised techniques, such as dusting with fingerprint powders or using chemical reagents to enhance visibility.
Furthermore, the size and condition of the fingerprint can pose challenges. Small or distorted prints may be difficult to identify and collect accurately, requiring expert analysis and specialised tools.
In some cases, partial or fragmented prints may be the only evidence available, further adding to the complexity of collecting and identifying fingerprints.
Overall, the process of collecting fingerprints at crime scenes is a complex task that requires attention to detail and expertise. Overcoming the challenges associated with different surfaces, environmental factors, latent prints and various fingerprint conditions crucial to ensure accurate identification and analysis for forensic investigations.
Identifying fingerprints at crime scene is a crucial task in forensic sciences. The process involves two main components: comparison and analysis of fingerprints, and the use of National Automated Fingerprint Identification Systems (NAFIS). Forensic experts play a vital role in this identification process.
They meticulously examine the patterns and details of fingerprints to determine matches. NAFIS technology has revolutionised the process by allowing for efficient and accurate identification of prints through computerised systems. however, challenges such as smudged or partial prints can make the identification process difficult.
Comparison and analysis of fingerprints play a crucial role in forensic science. By examining the unique ridge characteristics, patterns and minutiae points, experts can identify individual from their fingerprints.
There are three main types of fingerprints: loop patterns, whorl patterns and arch patterns.
Loop patterns have one or more ridges that enter from one side and exit from the same side, while whorl patterns have circular or spiral ridge configurations. Arch pattern on the other hand, have ridges that enter from one side and exit from the other side.
The comparison and analysis of these patterns help forensic experts in identifying fingerprints found at crime scenes accurately. By using magnification techniques and specialised software, they can carefully examine and match the patterns and minutiae points, providing valuable evidence for criminal investigations.

NAFIS has revolutionised the process of fingerprint identification at crime scenes. These systems use advance technology to scan and analyse fingerprints, matching them with a vast database to known prints.
NAFIS works by converting the unique ridge patterns of a fingerprint into digital minutiae points, which are then compared for potential matches. This automated method allow for quick and accurate identification, significantly reducing the time and effort required compared to manual analysis.
NAFIS also greatly improves the efficiency of criminal investigations by rapidly linking fingerprints found at crime scenes to known individuals in criminal databases. With the increasing integration of NAFIS in forensic sciences, law enforcement agencies can now quickly identify suspects and solve crimes more effectively.
The national-level NAFIS solution is implemented and managed by the Central Fingerprint Bureau (CFPB) at National Crime Records Bureau, New Delhi.
It will enable law enforcement agencies to upload, trace and retrieve information from the database 24x7 in real-time
The identification system aims to establish a robust online searchable national database of fingerprints from all states and UTs.
Forensic experts play a crucial role in fingerprint identification at crime scenes. Their expertise and knowledge are instrumental in analyzing and comparing fingerprints to find matches.
By carefully examining the patterns, ridges, and pores present in the prints, forensic experts can determine the type of fingerprint, such as loop patterns, whorl patterns, or arch patterns. They utilise specialised techniques and tools to collect and preserve fingerprints, taking care to avoid contamination or distortion.
The comparison and analysis of fingerprints require meticulous attention to detail and a deep understanding of the unique characteristics. In addition, forensic experts may use National Automated Fingerprint Identification Systems (NAFIS) to expedite the identification process.
Their expertise and dedication contribute significantly to the accurate and efficient identification of fingerprints, aiding in the investigation and resolution of crimes.
Advancements in Fingerprint Analysis Technology have revolutionised the field of forensic science. With the use of high-resolution scanners and advanced image processing algorithms, experts can now extract more detailed features from fingerprints, leading to more accurate identifications.
These advancements have also enabled the creation of comprehensive databases where fingerprints recovered from crime scenes can be compared against vast collections of known prints. Additionally, Chemical Methods for Developing Latent Fingerprints have become invaluable tools for investigators.
By using chemical reagents and processing techniques, latent prints can be made visible, expanding the pool of potential evidence.
These developments in fingerprint analysis technology and chemical enhancement methods have significantly enhanced the ability to identify fingerprints at crime scenes, providing crucial evidence for criminal investigations.
Advancements in Fingerprint Analysis Technology have revolutionized the field of forensic science. These advancements have significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of fingerprint identification at crime scenes.
One major breakthrough in this area is the development of National Automated Fingerprint Identification Systems (NAFIS). NAFIS uses advanced algorithms and computer software to compare and analyze fingerprints with an extensive database, enabling rapid and accurate identification of individuals.
Another noteworthy advancement is the use of chemical methods for developing latent fingerprints. These methods involve the application of specific chemicals that react with the components of sweat and oils present in fingerprints, making them visible for analysis.
These technological advancements have greatly enhanced the overall fingerprint identification process and have become invaluable tools for forensic experts in solving crimes.
Chemical methods play a crucial role in developing latent fingerprints left at crime scenes. These methods help enhance the visibility of latent prints, making it easier for forensic experts to identify and analyze them.
There are various chemical techniques used for developing latent fingerprints, including fingerprint powders, chemical reagents, and superglue fuming.
Fingerprint powders, such as black powder or magnetic powder, are commonly used to visualize latent prints on non-porous surfaces. The powder adheres to the sweat and oil residues left behind by the friction ridge skin, making the print visible to the naked eye or through photography.
Chemical reagents, like ninhydrin and DFO (1,8-Diazafluoren-9-one), are used to develop prints on porous surfaces. These reagents react with the amino acids present in sweat, creating a visualized print.
Superglue fuming, another chemical method, utilizes cyanoacrylate, a strong adhesive. When heated, cyanoacrylate reacts with moisture in the air and forms a white residue on the print. This makes latent prints visible and capable of further analysis.
These chemical methods for developing latent fingerprints provide crucial information in criminal investigations. By effectively utilizing these techniques, forensic experts can discover and analyze vital evidence, aiding in the identification and apprehension of criminals.
In conclusion, fingerprints play a crucial role in forensic science and crime scene investigations. They are unique to each individual and can provide valuable evidence in identifying suspects and solving cases.
The three main types of fingerprints – loop patterns, whorl patterns, and arch patterns – have distinct characteristics that help forensic experts classify and analyse them. Collecting fingerprints at crime scenes requires specific techniques and tools to ensure preservation for further analysis.
Identifying fingerprints involves detailed comparison and analysis, often with the help of national automated fingerprint identification systems (NAFIS).
Advancements in fingerprint analysis technology and chemical methods for developing latent fingerprints have greatly enhanced the accuracy and reliability of fingerprint identification techniques.
Overall, fingerprints continue to be a powerful tool in forensic investigations, aiding in the pursuit of justice.
I have been surfing online more than 3 hours today yet I never found any interesting article like yours It is pretty worth enough for me In my opinion if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you did the web will be much more useful than ever before
Simply wish to say your article is as amazing The clearness in your post is just nice and i could assume youre an expert on this subject Well with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post Thanks a million and please carry on the gratifying work
Fantastic site A lot of helpful info here Im sending it to some buddies ans additionally sharing in delicious And naturally thanks on your sweat
Hi my loved one I wish to say that this post is amazing nice written and include approximately all vital infos Id like to peer more posts like this
Somebody essentially lend a hand to make significantly posts I might state That is the very first time I frequented your web page and up to now I surprised with the research you made to create this particular put up amazing Excellent job
Leave a Reply