In the era dominated by digital technology, audio has become a fundamental medium of communication, information exchange, and entertainment. However, with the ease of audio recording and manipulation, the authenticity of audio recordings has come into question in various contexts, from legal proceedings and investigative work to journalism and content creation.
Audio authentication is the process of verifying the legitimacy, integrity and source of an audio recording. It is crucial discipline that seeks to ensure the reliability of audio evidence and the trustworthiness of the information conveyed through sound.
As audio technology continues to advance, so do the techniques used by individuals with malicious intent to alter audio recordings for purposes such as fraud, misinformation, or tampering with evidence. This underscores the pressing need for robust methods and tools to authenticate audio files, ensuring to scrutinise it for signs of tampering, inconsistencies or alterations.

The chain of custody for audio authentication is a crucial process that ensures the integrity and credibility of audio evidence in legal proceedings.
It is documented record of the handling, storage, and transfer of audio recordings from the moment they are collected or discovered to their presentation in court.
Here are the key steps in establishing a chain of custody for audio evidence:
1. Collection:
When the audio recording is first collected, it should be properly documented, including the date, time, location, and individuals involved in the collection. The recording device used should also be noted.
2. Sealing and labeling:
The audio recording should be placed in a tamper-evident container or evidence bag, sealed, and labeled with unique identifiers, such as case numbers, exhibit numbers, or barcodes. This helps prevent tampering and ensures proper tracking.
3. Initial custody:
The person who collected the audio evidence becomes the initial custodian and should maintain control over it. They must document any handling or access to the evidence.
4. Transfer of custody:
If the evidence needs to be transferred to another individual or location, this transfer should be documented, and the evidence should be sealed and labeled again to confirm its integrity.
5. Storage
The audio recording should be stored in a secure and controlled environment, such as an evidence locker or storage facility, to prevent unauthorised access or tampering. Access to the storage area should be restricted and logged.
6. Access and handling:
Anytime someone needs to access the audio evidence for analysis, authentication, or other purposes, this should be recorded, and the evidence should be resealed after use.
7. Analysis and authentication:
Experts or analysts should document their actions and findings during the examination of the audio evidence, ensuring transparency and accountability.
8. Court presentation:
When audio evidence is presented in court, the chain of custody documentation is used to establish its authenticity and credibility. This includes testimony from custodians and experts who handled the evidence.
Maintaining a well-documented chain of custody is critical to prevent contamination, tampering, or disputes regarding the authenticity of audio recordings. It helps ensure that the evidence remains admissible and trustworthy in legal proceedings.
Audio authentication is the process of determining whether an audio recording has been tampered with or edited in any way. In cases where audio evidence is presented in court or used in investigations, it is vital to establish its authenticity. This process helps in verifying the identity of speakers, detecting alterations, and confirming that the audio has not been manipulated.
1. Understanding Audio Authentication:
Audio authentication is the process of verifying the authenticity and integrity of an audio recording. This is crucial in legal, investigative, and other applications where the accuracy and reliability of audio evidence are paramount.
2. Metadata Inspection:
The journey of audio authentication begins with metadata. Metadata associated with an audio file, such as recording date, device used, and authorship information, can provide crucial insights. Inconsistencies or missing data can raise suspicion.
3. Listening to the Audio:
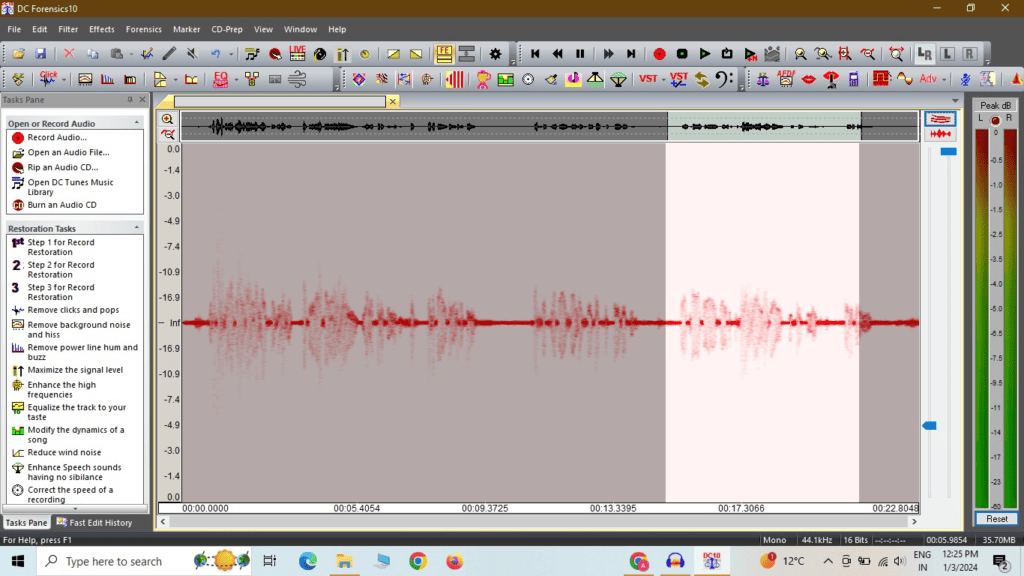
The first-hand auditory examination is essential. Listening to the recording with a trained ear can reveal obvious anomalies, unnatural gaps, or segments that sound edited.
4. Timestamp Analysis:
Reviewing timestamps and event sequences is crucial for detecting any discrepancies. Unusual time jumps or inconsistencies in the chronological order of events can suggest editing.
5. Spectrograms:
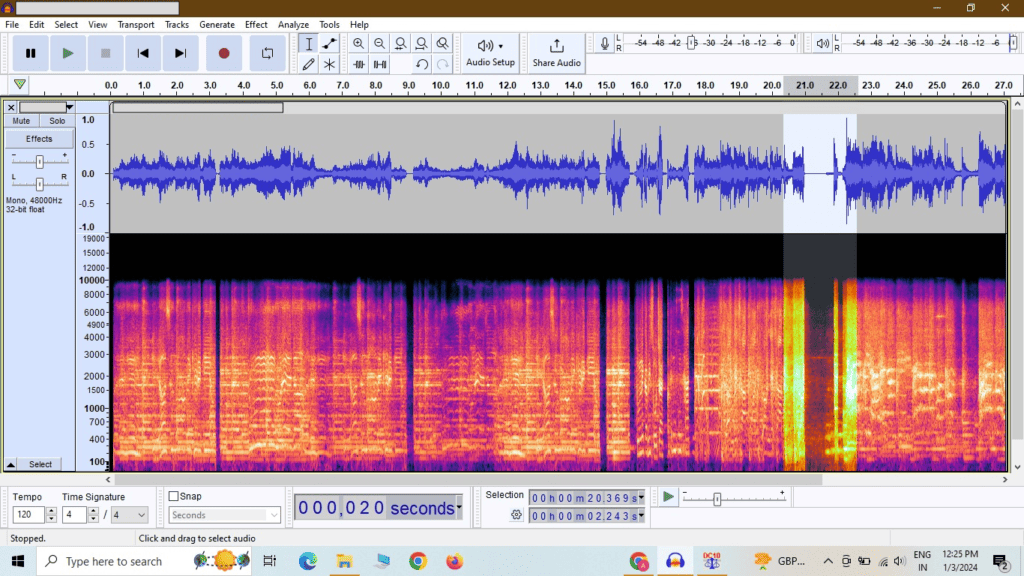
Spectrograms are a graphical representation of sound that displays the frequency content of an audio signal over time. They are created by breaking down the audio signal into its constituent frequencies and showing how they change over time. Spectrograms are powerful tools for detecting audio tampering as they reveal details not easily discernible by the human ear. For instance, they can expose hidden messages, alterations, or inconsistencies within an audio recording.
6. Frequency Analysis:
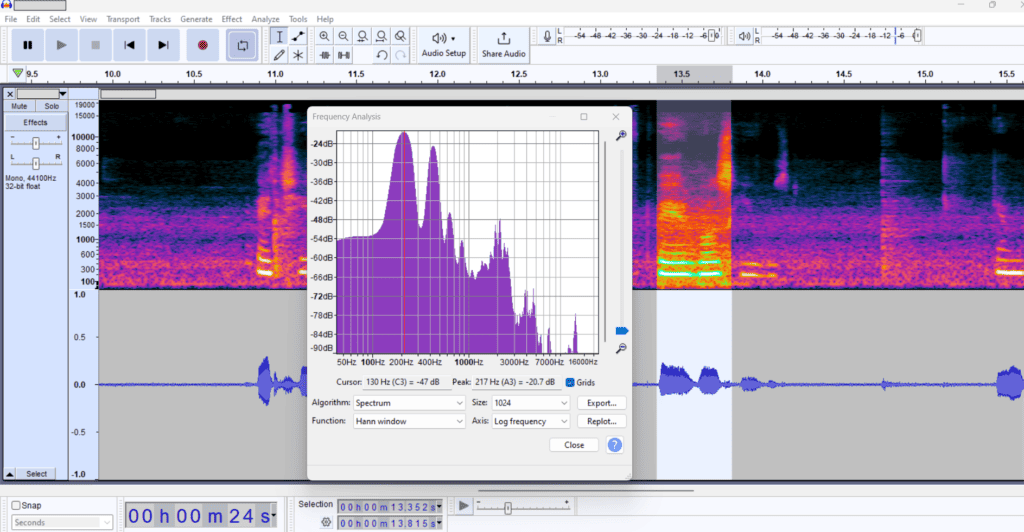
Unveiling Anomalies Frequency analysis involves examining the distribution of frequencies within an audio recording. This analysis can uncover inconsistencies, such as unusual spikes or gaps in the frequency spectrum, which may indicate tampering. Additionally, anomalies in the frequency domain can provide clues about the type of equipment used for recording or alterations made to the audio.
7. Noise Floor:
The noise floor is the level of background noise present in an audio recording when no sound is intentionally generated. Anomalies in the noise floor can signal tampering or editing. For example, abrupt changes in the noise floor may indicate splicing or cut-and-paste operations within the audio file.
8. Waveform Analysis:
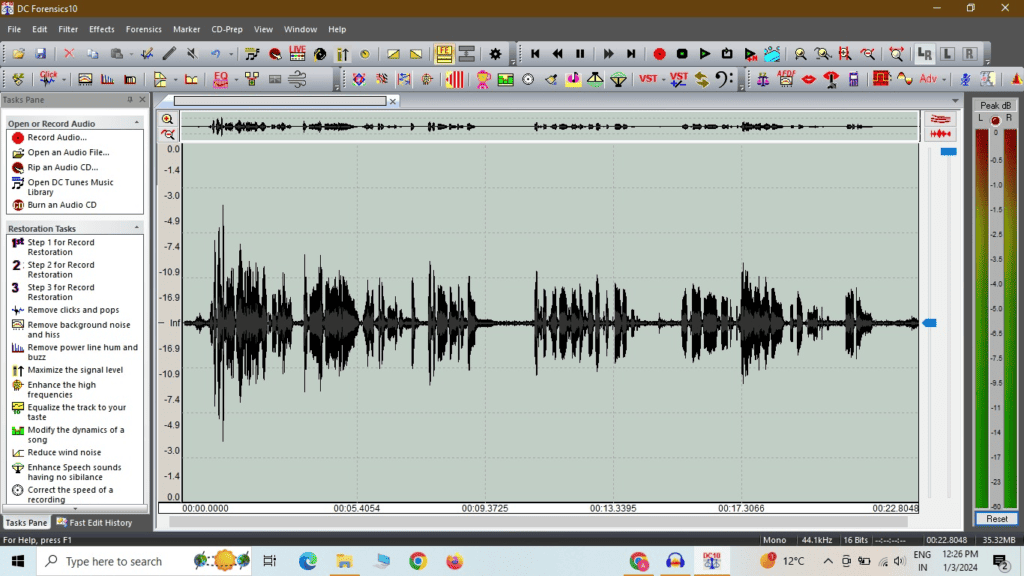
Examining the Shape Waveform analysis involves studying the shape of the audio signal itself. By looking at the waveform, experts can identify irregularities in the audio data. These irregularities might include gaps, discontinuities, or unnatural patterns, all of which can be indicative of tampering.
In the legal context, the findings of audio authentication are pivotal, influencing the admissibility of audio recordings in court. The involvement of forensic audio experts and the maintenance of a secure chain of custody further bolster the reliability of audio evidence. In a world where audio recordings have a significant impact on investigations, legal proceedings, and more, audio authentication is the safeguard that ensures trust and truth prevail.
Written by-
Ananshi Saini

Amazing post.
Just wanted to extend my heartfelt appreciation for the captivating read. Every bit of your recent article was truly enjoyable! Thank you for generously sharing your valuable insights.
Leave a Reply